How Starship's 150-Ton Payload Capacity Enables Interplanetary Journeys for 100 People 🚀🌌

SpaceX's Starship is a fully reusable spacecraft and rocket system designed to carry both crew and cargo to Earth orbit, the Moon, Mars, and beyond. It is the world's most powerful launch vehicle ever developed, with a payload capacity of 150 metric tonnes (330,000 pounds) to low Earth orbit in a fully reusable configuration.
Advertisement

This payload capacity is enough to carry everything needed for a long-duration, interplanetary journey for up to 100 people. This includes food, water, shelter, life support systems, and even vehicles.
In addition to its large payload capacity, Starship is also designed to be very efficient. It uses a new type of rocket engine called the Raptor, which is powered by methane and liquid oxygen. These fuels are much more efficient than the traditional fuels used by rockets, such as kerosene and liquid hydrogen.
This combination of large payload capacity and high efficiency makes Starship the ideal vehicle for interplanetary travel. It will allow us to send humans to Mars and other distant destinations for the first time.
Here are some of the specific ways in which Starship's 150-ton payload capacity will enable interplanetary journeys for 100 people:
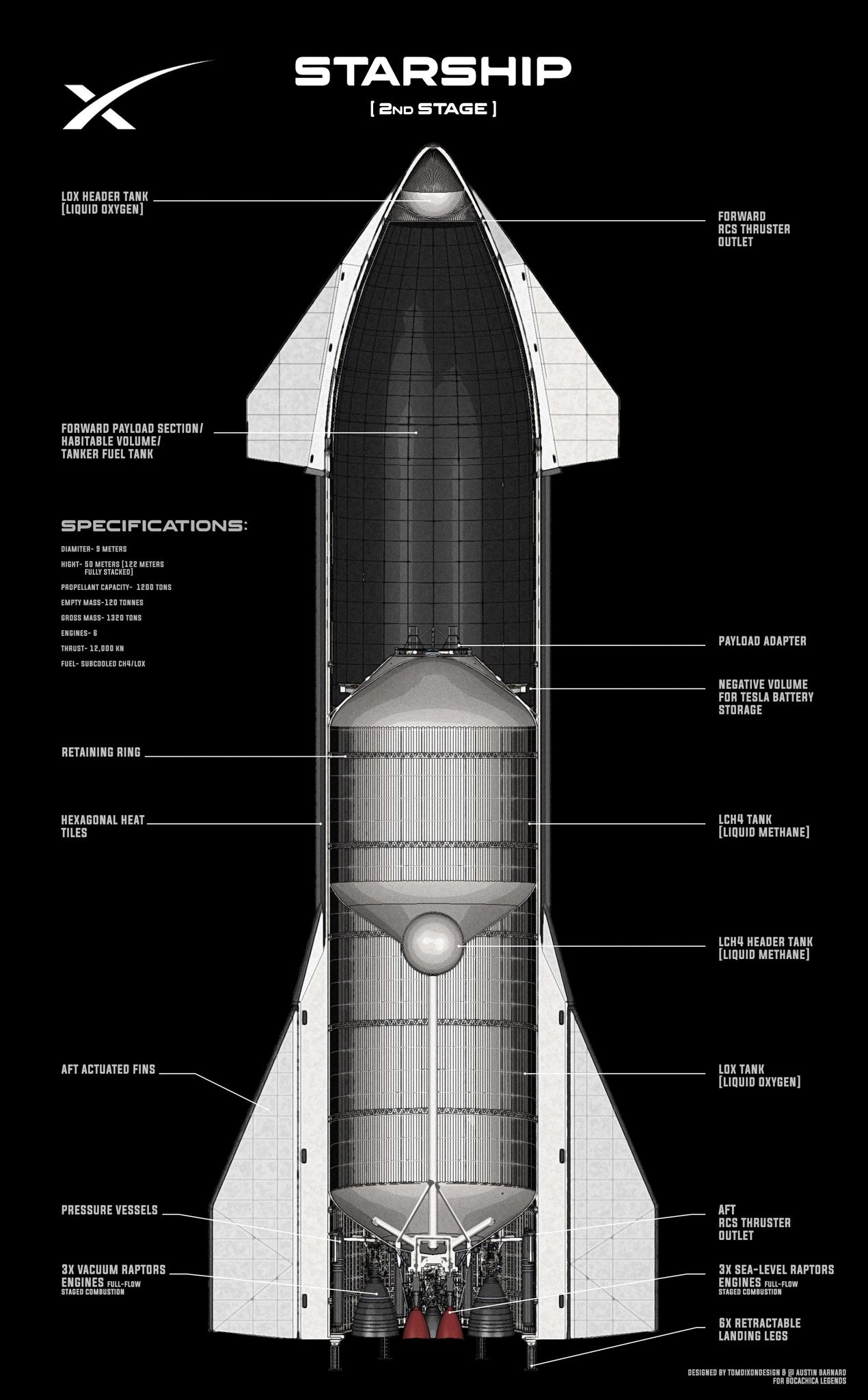
- It will allow us to carry enough food, water, and other supplies for a long-duration journey.
- It will allow us to carry enough life support systems to keep the crew alive during the journey.
- It will allow us to carry enough vehicles to transport the crew and supplies around the destination planet.
- It will allow us to carry enough equipment to build a base on the destination planet.
The development of Starship is a major step forward in the exploration of space. It will allow us to travel to destinations that were previously out of reach, and it will help us to establish a permanent presence in space.
In addition to its potential for interplanetary travel, Starship could also be used for other purposes, such as:
- Delivering large satellites into orbit
- Building space stations
- Mining asteroids
- Tourism
The possibilities are endless. Starship is a truly revolutionary spacecraft that has the potential to change the way we explore space.
Advertisement
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Starships:
Q1: What is a starship?
A1: A starship is a type of spacecraft designed for interstellar travel, allowing it to journey between stars within a galaxy.
Q2: How does a starship differ from other types of spacecraft?
A2: Starships are typically designed for long-duration space travel and are equipped with advanced propulsion systems to achieve near-light speed, enabling them to cover vast interstellar distances.
Q3: Are starships a reality today, or are they primarily a concept in science fiction?
A3: As of my last knowledge update in September 2021, starships are primarily a concept in science fiction. While humanity has developed spacecraft for space exploration, we have not yet built starships capable of interstellar travel.
Q4: What are some famous examples of starships in science fiction?
A4: Some famous examples include the USS Enterprise from "Star Trek," the Millennium Falcon from "Star Wars," and the Heart of Gold from "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy."
Q5: Is interstellar travel feasible with current technology?
A5: Interstellar travel is currently beyond our technological capabilities due to the immense distances involved and the limitations of our propulsion systems.
Q6: Are there any real-life initiatives or research projects related to starship development?
A6: Yes, some organizations and initiatives, like the Breakthrough Starshot project, are researching advanced propulsion methods for potential interstellar travel in the future.
Q7: What are some of the challenges associated with building a functional starship?
A7: Challenges include developing propulsion systems capable of reaching near-light speed, addressing the vast distances between stars, finding ways to sustain life during long journeys, and protecting against cosmic radiation.
Q8: Can starships travel faster than the speed of light, as depicted in some science fiction?
A8: According to our current understanding of physics, traveling faster than the speed of light is not possible. Science fiction often employs theoretical concepts like warp drives or hyperspace to overcome this limitation.
Q9: Are there any theoretical concepts or ideas for achieving interstellar travel?
A9: Some theoretical concepts include the Alcubierre "warp" drive, which warps spacetime around a spacecraft, and using laser propulsion for extremely high-speed travel.
Q10: What would be the purpose of interstellar travel with starships?
A10: The primary purposes could include scientific exploration, the search for extraterrestrial life, resource acquisition, or the survival of humanity in the event of a catastrophic event on Earth.
Q11: Are there any proposed missions or plans for future interstellar travel?
A11: As of my last update, there were no concrete plans for interstellar missions. However, discussions and theoretical studies on the topic continue within the scientific community.
Q12: Can starships be used for space colonization?
A12: Starships could potentially be used for space colonization by transporting humans to distant star systems where habitable planets may exist. However, this remains a hypothetical scenario for now.
Q13: What are some notable books or articles about starships and interstellar travel?
A13: Some notable works include "Interstellar" by Kip Thorne, "Tau Zero" by Poul Anderson, and various scientific papers on advanced propulsion methods.
Q14: Are there any ethical or moral considerations associated with starship travel and space exploration?
A14: Ethical considerations may include the potential impact on other life forms, the responsibility to protect the environments of other planets, and questions related to the equitable distribution of resources.
Q15: When might humanity realistically achieve interstellar travel with starships?
A15: Predicting when humanity might achieve interstellar travel is highly speculative. It depends on technological advancements and breakthroughs that may occur in the future.