SpaceX explains how it is reducing the brightness of Starlink satellites.

Monday, August 1, 2022 | Chimniii Desk
SpaceX explained how it is reducing the brightness of its Starlink satellites. The space exploration corporation describes how it is collaborating with the astronomy community to lessen light pollution in a document titled Brightness Mitigation Best Practices for Satellite Operators.
Advertisement
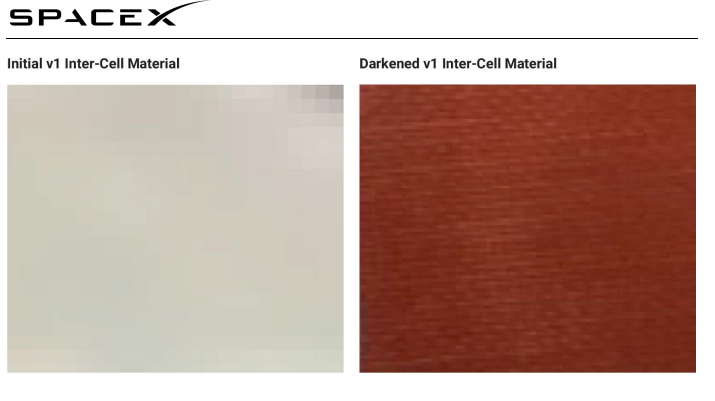

The inter-cell backing material was another thing that SpaceX changed on its first-generation satellites. Originally white, SpaceX altered the material to a dark red colour that lessens the brightness of the arrays.
The material's darkening has the drawback of raising the solar array's temperature, which lowers performance. However, in order to lessen the brightness of the satellites, SpaceX will use a variety of designs, including this one.
Advertisement
Astronomers have criticised SpaceX for the Starlink satellites' brightness. In addition to paying attention to the criticism, Elon Musk and the SpaceX crew are actively responding by working with the astronomy community to address the problem.
STARLINK SATELLITES WILL BE MADE INVISIBLE TO THE UNAIDED EYE BY SPACEX.
According to SpaceX, the collaboration allowed it to pinpoint and address the main factors contributing to satellite brightness. In order to make the satellites undetectable to the human eye when they are at their normal operational height, the company is working on this.
Observers on earth may be able to see satellites if they are backlit by the sun at night. Any satellite's visibility, however, is influenced by the materials that were utilised to construct its surfaces.
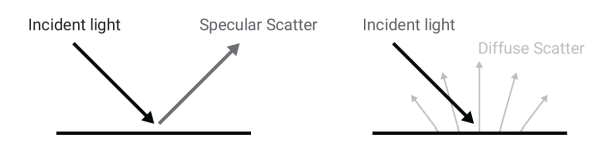
Since satellites don't produce any light of their own, the brightness comes from sunlight reflecting off their surfaces and down to earth. Specular or diffuse scattering are the two possible types of light scattering.
SPACEX IS SPECULATING ON SCATTER
Advertisement

Credit: Spacex
Advertisement
Specular surfaces are a focus for SpaceX. Similar to a mirror, specular light only reflects at one angle. Diffuse light reflects in numerous directions. The illustration above demonstrates how diffuse and specular light disperse differently.
Not all materials are extremely reflective; some can absorb light or make the light that is reflected appear significantly less bright, according to SpaceX.
There are two ways to see SpaceX's satellites from the ground.
- Sunlight reflects off the body's surface.
- Sunlight reflects off the solar panels.
SpaceX adopted mitigations for both issues for its first-generation satellites currently in operation in order to fix this.
RF-TRANSPARENT MIRROR FILMS AND SUN VISORS
Advertisement

Advertisement
Credit:Spacex
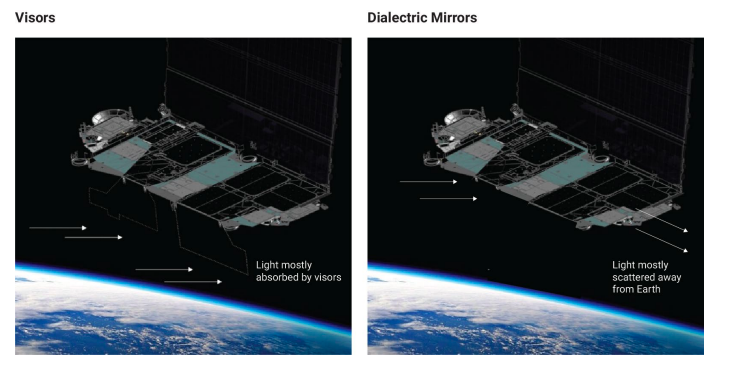
Sun Visors
SpaceX created sun visors for the first-generation satellites that prevent sunlight from striking the chassis's bottom side (body of the satellite.) Engineers created materials for their creation that are radio frequency invisible.
The laser links that SpaceX uses to extend coverage to far-off parts of the earth were, however, obstructed by the sun visors. The satellites experienced severe drag as a result of the visors. So, SpaceX came to the conclusion that the sun visors weren't a practical long-term fix.
RF- transparent mirror films.
Sun visors were replaced by RF-transparent mirror sheets, which SpaceX created. Most of the sunlight is scattered away from the Earth by the coating. According to SpaceX, it has been enhancing its mirror sheets to reduce light scattering back to earth.
It intends to use its next-generation satellites to broadcast an updated version of the movie.
Advertisement

Advertisement
STARLINK SATELLITE DIELECTRIC MIRROR FILM
SpaceX stated that their next-generation satellite will increase the Starlink network's capacity and connect more people in more locations.
I'll focus on one of the three cutting-edge brightness approaches that the second-generation satellites will employ: Dielectric Mirror film.
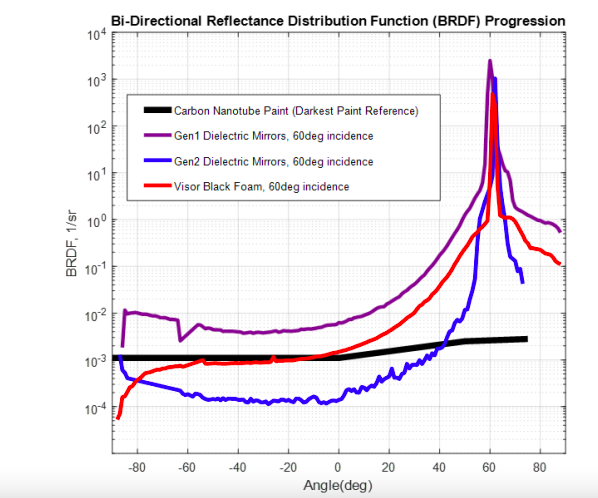
The satellites' undersides will be covered with a second-generation dielectric mirror film by SpaceX. By employing a Bi-Directional Reflectance Distribution Function (BRDF) metric, this version reduces the observed brightness ten times better than the first-generation film.
The chart below illustrates how the BRDF affects visibility.
Advertisement

Advertisement
SpaceX increased the film's specular scatter through intensive research and testing. The Bragg mirror at the centre of the film is made up of numerous thin layers of plastic with various refractive indices that interact internally to reflect light in interference patterns.
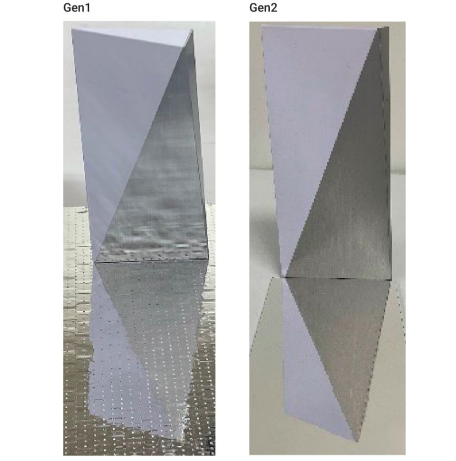
Additionally, radio waves can easily travel through it with no problems. Thin, pure coatings of titanium dioxide and silicon dioxide that don't alter the film itself were applied as protective layers to shield it. A comparison of the first- and second-generation mirrors may be found below.
Advertisement

Advertisement
THE DIELECTRIC MIRROR FILM WILL BE AVAILABLE FROM SPACEX AS A PRODUCT.
The dielectric mirror film will be made available by SpaceX as a product on the Starlink website. The cause is that SpaceX cannot, by itself, lessen the impact of satellites on space exploration.
All operators will be allowed to use the movie at no cost to them in order to lessen the impact of their own constellations.
The ASTRONOMY COMMUNITY AND SPACEX WILL CONTINUE TO WORK TOGETHER
SpaceX stressed the significance of the astronomy community's efforts and its commitment to working with them to minimise the negative consequences of all satellite operations.
Starlink will enable SpaceX to connect as many people as possible, enhancing the lives of millions of people on Earth.
"SpaceX is a significant supporter of astronomy and the scientific community as a space exploration enterprise."
Advertisement